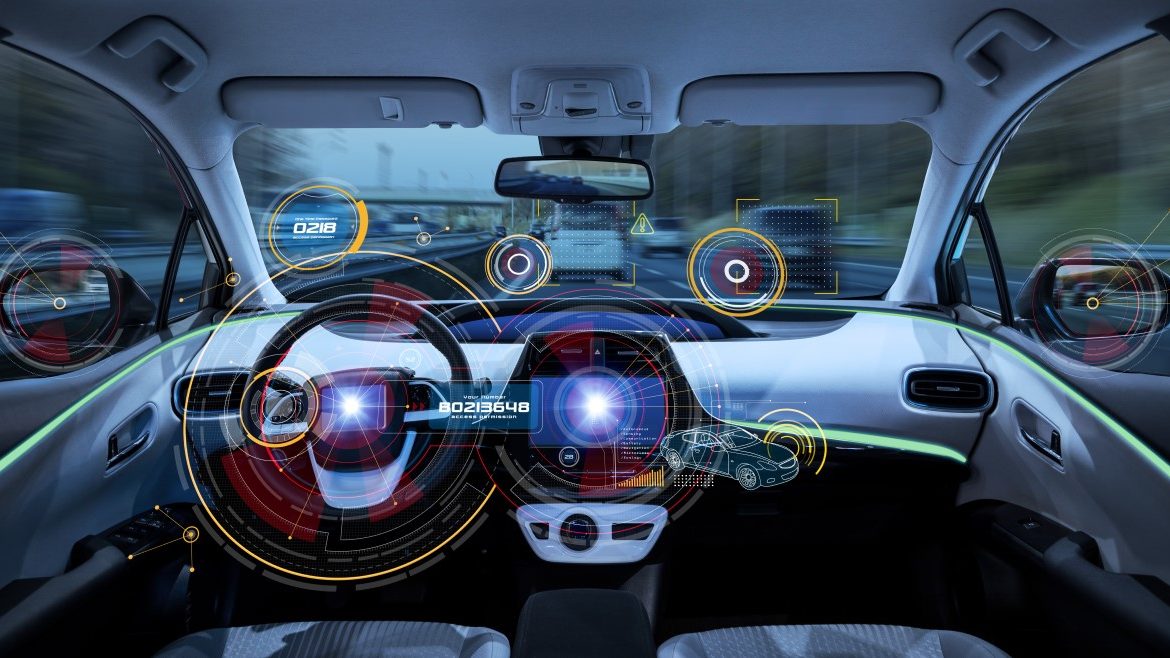
To fix and detect potential vehicle malfunctions and validate and update in-car software without any downtime, Tel Aviv-based start-up Aurora Labs has made a remote and proactive system.

Modern cars are quickly resembling sophisticated computers on wheels. It happens even before autonomous vehicles become a regular sight in our streets.
One hundred fifty million lines of code have increasingly connected vehicles. To land Apollo 11 on the Moon in 1969, it had 145,000 lines. Self-driving cars might require having up to one billion lines of code.
Vehicles running on software rather than just machines represent a unique system of highly complex mobility for passengers, manufacturers, and repair shops. Checking the tires, brakes, and engine to find a solution to the problem will probably no longer suffice.
A Tel Aviv-bases start-up, Aurora Labs developed software called a “self-healing car.” They are seeking to build trust in the new generation of automotive innovation. To fix potential vehicle malfunctions, validate and update in-car software, it will be a proactive and remote system.
Ori Lederman, the Aurora Labs co-founder, told the Jerusalem Post that the automotive industry faces a significant revolution. The main issue Lederman faces is if drivers will trust the car, even before they hand over complete autonomy to it. It is a big challenge for carmakers.
Moreover, Lederman added that the challenges include whether problems can be solved securely and safely. Whether solving defects without interrupting car use is possible. And lastly, whether the detection of software issues can occur after selling a vehicle.
However, due to software-based defects alone, some eight million vehicles were recalled in the United States in 2018.
Ordman and Lederman about the vehicles

Roger Ordman, Executive Vice President of Marketing, said that before the human passes out, its body can detect something is wrong. It is the auto-immune system that indicates something is not working correctly. Thus it suggests how to fix it: white blood count increases or the temperature rises. Sometimes the body needs an external intervention, and sometimes the body can do a self-fix.
The company’s Line-Of-Code behavior technology creates a deep understanding of the installed software in over 100 vehicle Engine Controls Units (ECU) and the relationship between them. Artificial intelligence and machine learning powers. The software can enable remote updates alongside the detection of software faults. It is possible with the help of over-the-air software updates.
Ordman added that car manufacturers would be able to improve the software running on connected vehicles continuously. Similarly, silent updates automatically realize through smartphone applications. The manufacturers will need to meet stringent regulations concerning cybersecurity and “over-the-air” updates, developed by bodies including the UNECE.
Lederman said that when they started developing the idea and joined forces, they knew their technology applied to any smart, connected device would be beneficial. In the automotive industry, the need for managing, recovering, detecting, and being transparent about software is by far the most considerable. They made a transition from mechanical parts to virtual systems with the help of lines of code. The invention will have a big future in the automotive industry.